
Recently, Professor Chen Jun's team from Sun Yat-sen University and Jinfeng Laboratory wereScience ImmunologyA research paper entitled "PSGL-1 is a phagocytosis checkpoint that enables tumor escape from macrophage clearance" was published. This study revealed for the first time the functional mechanism of PSGL-1 on tumor cells to promote tumor immune escape by inhibiting the phagocytosis of macrophages, elucidating the new function of PSGL-1 molecules as macrophage phagocytosis checkpoints, and providing new targets and new strategies for macrophage immunotherapy.

This study found that PSGL-1 is highly expressed on a variety of malignant tumor cells, and its expression level is negatively correlated with the patient's prognosis. By constructing multiple mouse tumor models, it was found that specific knockout of tumor cells PSGL-1 enhanced the phagocytosis of macrophages on tumor cells, significantly inhibited tumor development, and prolonged the survival of tumor-bearing mice. Through exploration of the mechanism, tumor cell PSGL-1 can inhibit the binding of tumor ICAM1 to macrophage LFA-1, thereby inhibiting the phagocytosis response. Knocking out PSGL-1 activates the downstream prophagocytosis signaling pathway of LFA-1, and then induces cytoskeleton recombination through the Src/Syk/PI3K signaling axis, ultimately enhancing the phagocytosis function of macrophages. In terms of treatment strategies, humanized monoclonal antibodies against PSGL-1 showed good safety in cynomolgus monkey toxicology experiments, and no obvious toxicity was found. In vitro functional experiments, this antibody can significantly enhance the phagocytosis of macrophages on human malignant tumor cells ; In tumor model treatment, PSGL-1 antibody can effectively inhibit tumor progression and show significant synergistic effects with chemotherapy, CD47 antibody and CD38 antibody therapy. This study provides new possibilities for the clinical treatment of malignant tumors.
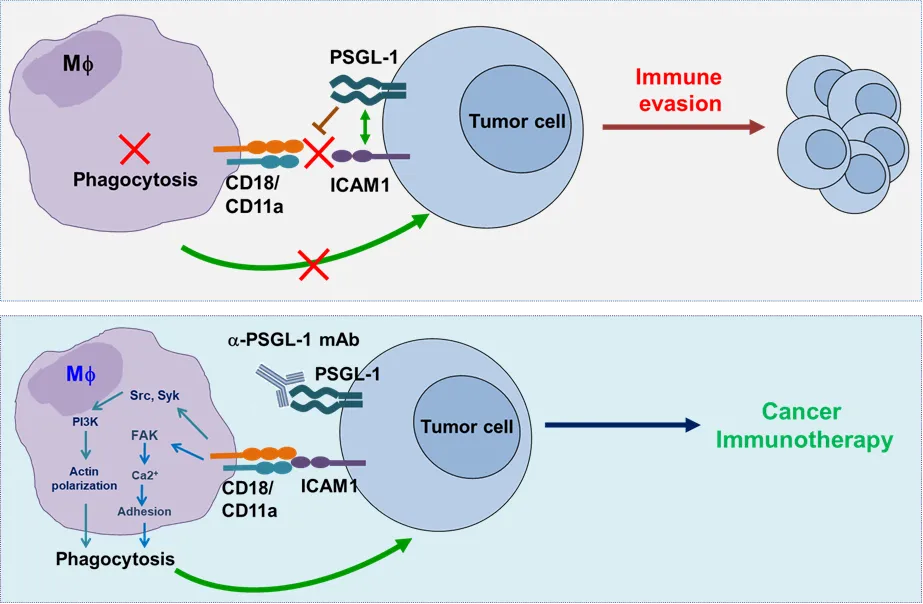
▲Schematic diagram of the mechanism of this research work. As a new phagocytosis checkpoint, PSGL-1 weakens the phagocytosis of macrophages by inhibiting the binding of ICAM-1 and LFA-1, revealing a new mechanism of immune escape from malignant tumors. Antibodies targeting PSGL-1 are new safe and effective immunotherapy strategies for tumors.
Science Immunology, published by AAAS (Asian Association for the Advancement of Science), covers a wide range of areas from basic immunology to immune effects in health and disease. In 2025, the impact factor of journals reached 16.3. In the JCR partition, journals are located in the Q1 area of Immunology (IMMUNOLOGY) category. ; In the upgraded version of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in March 2025, it is a district 1 in major disciplines, medicine and minor disciplines, and is a top journal, providing global scientific researchers with a high-end platform to showcase cutting-edge research.
Click on the lower left to read the original text and access the original text link.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.5c02492