
Recently, Academician Bian Xiuwu, Academician of the Southwest Hospital of the Army Medical University and Professor Ping Yifang, worked in a team of professors from Ping Yifang, published a research paper titled "FAM50A drives breast cancer brain metastasis through interaction with C9ORF78 to enhance ʟ-asparagine production" in the international journal Science Advanceds (TOP journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Impact Factor: 12.5).

Primary breast cancer has achieved a better 5-year survival due to the advancement of treatment methods. However, the occurrence of metastasis poses great challenges to the survival of patients. Despite significant progress in targeted therapies and immunotherapy in modern medicine, the control of metastatic lesions remains a difficult task.
Bone, lung, liver and brain are four common metastases in breast cancer. Breast cancer brain metastasis (BCBM) accounts for 10–30% of all metastatic breast cancer cases, is associated with adverse prognosis, and impairs patients' cognitive and sensory function, resulting in severe limitations in quality of life (1). Currently available treatments for BCBM patients include surgery, whole-brain radiation therapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, and chemotherapy, or the combination of these therapies. However, life expectancy in BCBM patients remains unsatisfactory due to the blood-brain barrier limiting drug permeability and chemotherapy resistance (2). Therefore, it is urgent to clarify the molecular mechanisms of BCBM to find new therapeutic targets, improve therapeutic effects and improve the prognosis of BCBM patients.
The study found and identified FAM50A, the key molecule that regulates brain metastasis in breast cancer. Multiple experimental evidence shows that FAM50A promotes the occurrence of brain metastasis in breast cancer, and knocking out can significantly inhibit the occurrence of brain metastasis, allowing model mice to obtain better brainless metastasis survival. Further research reveals its mechanism of action: FAM50A promotes the expression of downstream molecule ASNS through interaction with C9ORF78. The latter is an asparagine synthetase, which promotes the increase in asparagine levels in breast tumor cells, which further enhances its brain metastasis ability. In the transformational sense, this study found that asparaginase, a drug originally used to treat leukemia, significantly inhibited the occurrence of brain metastasis in breast cancer by reducing asparagine levels in mice. This study confirmed that breast cancer brain metastasis relies on high levels of asparagine, filling the gap in the research direction of amino acid dependence in the field of breast cancer brain metastasis.
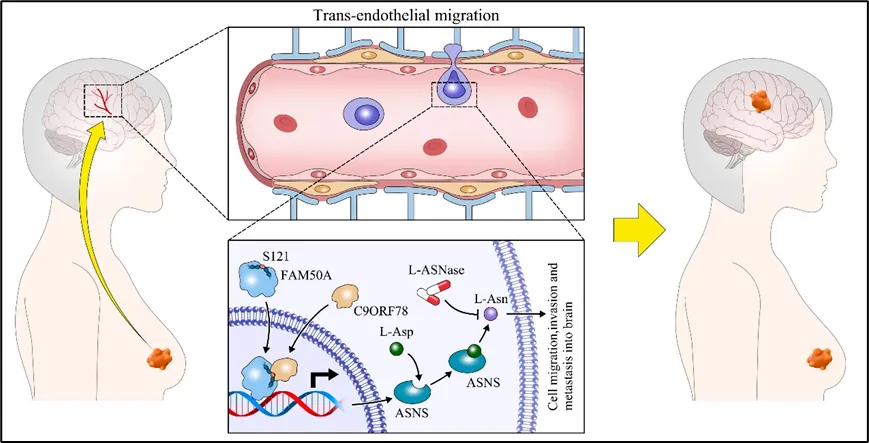
▲Schematic diagram of the mechanism of this research work. The FAM50A-C9ORF78-ASNS signaling pathway is a new therapeutic target for brain metastasis in breast cancer. Targeting this pathway or using asparaginase has the application potential to inhibit brain metastasis, providing new ideas for the prevention and control of brain metastasis in breast cancer patients.
References:
1. Kanchan RK, Siddiqui JA, Mahapatra S, Batra SK, and Nasser MW. microRNAs Orchestrate Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis: Advances in Therapy. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):29.
2. Wang Y, Ye F, Liang Y, and Yang Q. Breast cancer brain metastasis: insight into molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Br J Cancer. 2021;125(8):1056-67.
Science Advances is published by the AMER ASSOC ADVANCEMENT SCIENCE. It is an open-access journal focusing on multidisciplinary fields, covering various disciplines and interdisciplinary research directions, with content that takes into account in-depth research within disciplines and interdisciplinary innovation achievements (such as influential research papers and reviews in various fields). The latest impact factor of journals in 2025 is 12.5, and it is Q1 in the JCR area. The Chinese Academy of Sciences’ upgraded version of the “Comprehensive Journals” in major and minor disciplines in March 2025 are both located in District 1, and are top journals. It is an important platform for global scientific researchers to publish influential research results.
Click on the lower left to read the original text and access the original text link.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.5c02492